2022-08-05每日一题:623. 在二叉树中增加一行
2022-08-05
2分钟阅读时长
2022-08-05每日一题:623. 在二叉树中增加一行
给定一个二叉树的根 root 和两个整数 val 和 depth ,在给定的深度 depth 处添加一个值为 val 的节点行。
注意,根节点 root 位于深度 1 。
加法规则如下:
- 给定整数
depth,对于深度为depth - 1的每个非空树节点cur,创建两个值为val的树节点作为cur的左子树根和右子树根。 cur原来的左子树应该是新的左子树根的左子树。cur原来的右子树应该是新的右子树根的右子树。- 如果
depth == 1意味着depth - 1根本没有深度,那么创建一个树节点,值val作为整个原始树的新根,而原始树就是新根的左子树。
示例 1:
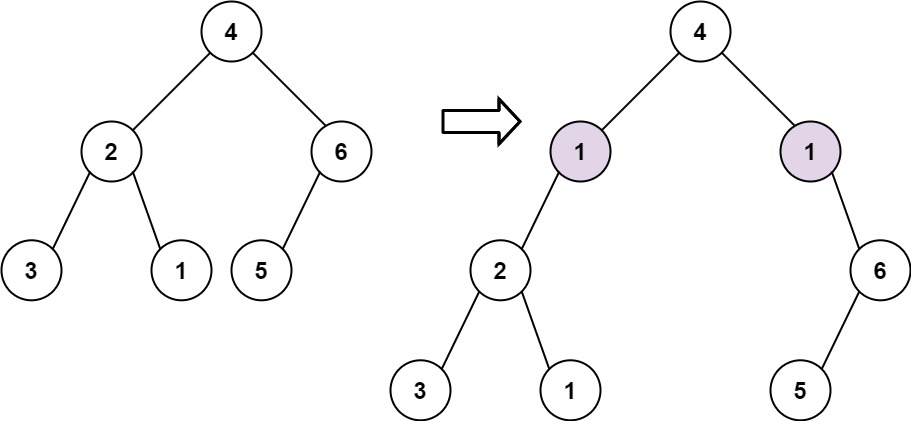
输入: root = [4,2,6,3,1,5], val = 1, depth = 2 输出: [4,1,1,2,null,null,6,3,1,5]
示例 2:
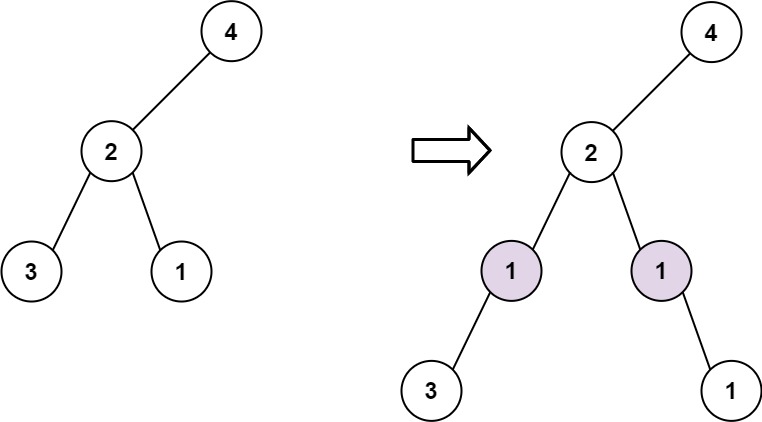
输入: root = [4,2,null,3,1], val = 1, depth = 3 输出: [4,2,null,1,1,3,null,null,1]
提示:
- 节点数在
[1, 104]范围内 - 树的深度在
[1, 104]范围内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100-105 <= val <= 1051 <= depth <= the depth of tree + 1
方法一:深度优先遍历
当depth 为 1 时,需要创建一个新的 root,并将原 root 作为新 root 的左子节点。
当depth 为 2 时,需要在root 下新增两个节点left 和 right 作为root 的新子节点,并把原左子节点作为left 的左子节点,把原右子节点作为 right 的右子节点。
当 depth 大于 2 时,需要继续递归往下层搜索,并将 depth 减去 1,直到搜索到 depth 为 2。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func addOneRow(root *TreeNode, val int, depth int) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return root
}
if depth == 1 {
return &TreeNode{Val: val, Left: root}
}
if depth == 2 {
root.Left = &TreeNode{Val: val, Left: root.Left}
root.Right = &TreeNode{Val: val, Right: root.Right}
} else {
root.Left = addOneRow(root.Left, val, depth-1)
root.Right = addOneRow(root.Right, val, depth-1)
}
return root
}
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为输入的树的节点数。最坏情况下,需要遍历整棵树。
空间复杂度:O(n),递归的深度最多为 O(n)。
方法二:深度优先遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func addOneRow(root *TreeNode, val int, depth int) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return root
}
if depth == 1 {
return &TreeNode{Val: val, Left: root}
}
queue := []*TreeNode{root}
for i := 0; i < depth - 2; i++ {
for n := len(queue); n > 0; n-- {
node := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
if node.Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Right)
}
}
}
for _, node := range queue {
node.Left = &TreeNode{Val: val, Left: node.Left}
node.Right = &TreeNode{Val: val, Right: node.Right}
}
return root
}
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为输入的树的节点数。最坏情况下,需要遍历整棵树。
空间复杂度:O(n)),数组空间开销最多为 O(n)。